Introduction
Measuring the success of your product and strategies is the challenging stage after execution. With a diverse set of customer success metrics to track, it’s easy to get distracted rather than hitting the bull’s eye.
Most of the time, you don’t even need to track each one of them available to you. The choice of your metrics depends upon your company’s stage and other goals.
But shortlisting a couple of customer success metrics can be tiresome. So we’ve done the digging for you and in this blog, we’ll cover:
In this blog, we’ll cover
- What are customer success metrics?
- How do you measure customer success?
- Customer health metrics
- Financial metrics
- Customer onboarding metrics
- Customer retention Metrics
What are customer success metrics?
Customer success is a crucial concept in growth and upscaling your SaaS business it generally revolves around customer retention and your product usability. An evolving company must focus equally on acquiring new customers and at the same time pay more heed to customer retention.
A marginal loss in users can compound over to a significant churn rate every month. SaaS is a recurring service model, and renewals play a significant role. Tracking customer success metrics can benefit your business with better renewal rates, less churn and improved net promoter score (NPS).
How do you measure customer success?
To measure the customer success of any organization, you need a quantitative assessment attached to that goal. Because you cannot measure or track anything that’s not measurable. And customer success metrics help you to track that goal with numerical ability. However, metrics and their importance can vary for different companies according to their goals and strategies.
To make it easier for you we have listed some prominent customer success metrics that allow you to track your progress and results seamlessly.
{{banner-customerdocs="/banner-ads"}}
Customer health metrics
1. MRR/ARR
Monthly Recurring Revenue(MRR) is a metric that denotes your net monthly recurring revenue. Similarly, Annual Recurring Revenue(ARR) is the revenue averaged out over one year.
Both metrics can be used to get a clear idea of your monthly and annual revenue. For ARR to be relevant for your business, your subscriptions must last for a year.
A point worth noting here — MRR and ARR are long-term metrics and these don't include any one-time subscription or purchase.
These metrics can be calculated by:

2. Revenue churn rate
Revenue Churn rate (a.k.a MRR Churn rate) is a basis to calculate net monthly revenue lost due to downgraded subscriptions and churned customers. This metric calculates how well you are retaining subscriptions for your product.
It answers the question, how much MRR did we lose the previous month? And your answers speak about the long-term health of the company as a SaaS business.
Most people think the revenue churn rate is similar to customer churn. But the distinction between them is customer churn is the percentage of those customers who’ve canceled their subscription in a given time frame.
It is given by:

3. Customer health score
Customer health score helps you to map out the crucial data regarding your customers and predict their behavior over a period of time. You can also use it to identify healthy customers and upscale your revenue with the help of add-ons.
It acts as an important factor in time management. Businesses can spend their effort and energy on users unlikely to churn on the basis of customer health scores. This prevents over-servicing accounts likely to churn no matter what.
Health score can be determined using the following equation:
Customer Health Score = total action value #n + total action value #n+1 + ……
where Total action value#n = action impact × action occurrence in a time
Range of health score for your business.
- a negative score = very sick (in high risk of churn)
- score between 1 - 40 = sick
- a score between 41 - 70 = a bit healthy
- a score between 71 - 100 = very healthy
- a score above 100 = thriving (users who are likely to upgrade)
4. NPS
Net promoter score or NPS denotes and tracks a vital factor: loyalty and customer satisfaction. Potentially loyal customers are related to a low churn rate and can help you achieve higher average monthly revenue.
It also identifies whether your product is used to its optimum, solving pain points and providing value to users. Major advantage of NPS over any other metric is it directly interacts with users on the frontend. This results in proportionate calculation of users satisfied with your product.
Based on the scale, it can classify users as:
- Promoters — People responding with a 9 or 10.
- Passives — People choosing a 7 or 8.
- Detractors — Anyone is responding with 6 or below.
5. Product stickiness
Product Stickiness is defined as the ratio of Daily Active Users (DAU) and Monthly Active Users (MAU) to calculate user engagement and how captivating a product is. This metric essentially defines product usability and identifies important future updates.
This metric is important as it reduces the risk of churn, increases upsell opportunities, and is directly related to ease of customer acquisition. It indirectly increases your growth and capacity to spend more in order to onboard new users.

Financial metrics
6. Revenue retention rate
Revenue retention rate can be termed as the total revenue from existing customers over time, including sales of add-ons, upgrades, downgrades, and cancellations. This metric demonstrates the churn rate and retention rate of existing users.
It is generally related to how well a business is doing in terms of providing quality, not losing customers to competitors and even neutralizing the effect of churn through repeat services.
The formula for calculation of Revenue Retention Rate:

7. Revenue churn rate
As discussed earlier, the revenue churn rate (a.k.a MRR Churn rate) is a basis to calculate net monthly revenue lost due to downgraded subscriptions and churned customers.
This metric calculates the churn rate in different categories of users i.e. high spenders and relatively lower ones. If a business’ revenue model uses dynamic pricing, then this metric can identify the segment which contributes significantly towards churn.
A simple formula can calculate it:

8. Renewal rate
Renewal Rate depicts the number of users renewing their product/service subscriptions and solely defines the retention rate of customers. This metric is calculated at the end of a subscription period to analyze customer churn and improve revenue.
It is given by:

9. CLV
Customer lifetime value determines the value of a user not just in terms of purchases/renewals but also the overall relationship. It is an important metric in projecting sales revenue and determines financial factors like budgeting, profitability and resource planning.
It is very critical to monitor CLV of users as positive growth ensures consistent revenue generation and projections. Apart from this, it also determines the efficiency of your marketing and indicates customer loyalty.
A simple formula can calculate it:
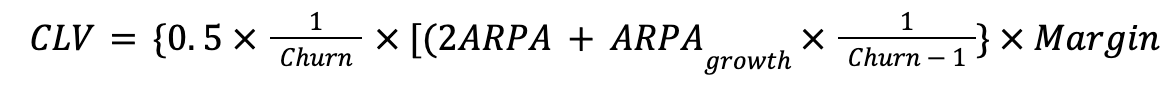
where:
ARPA = Average Rate per Account
Customer onboarding metrics
10. Time to value
Time to value refers to the duration when the user achieves their expectations from your product/service. In the SaaS world, the shorter the time to value the lower is the customer churn. This metric lets you improve your overall customer satisfaction and leads to customer retention. Entire onboarding efficiency and its success can also be derived using this metric.
11. Customer call drop-offs
Customer call drop-offs is a metric used to calculate the efficiency of your customer onboarding skills. It can attract revenue and customers related to your product/service when handled correctly. It adds value to the overall onboarding experience of the customer. Measuring the average call drop-offs can help you understand your customer experience's success.
12. Active user count
Active User count can be calculated using two metrics, i.e. DAU and MAU.
As the name suggests, Daily Active users are the sum of new users and existing users taking action using your service/product. Monthly Active Users aggregate new customers and existing customers over a month.
These metrics depict the effectiveness and health performance of your business. In terms of revenue, a healthy count of active users (daily/monthly) leads to increased sales and stable revenue streams.
13. Session time or length
Session time refers to the average duration a user dedicates to your website or application, and it is a metric used to calculate user engagement. When combined with other factors, it can be used to depict whether your product/service is imparting actual value to your customer.
It is important that a user spends a large proportion of his day on your product/service in order to add value to his work. Higher engagement also leads to increased cross-sales and up-sales.
It is calculated using:

Customer retention metrics
14. Customer retention rate
Customer retention rate refers to the rate at which customers stay with the business for the given period of time. It includes all strategies and activities businesses perform to retain customers and reduce churn.
It is an important metric for stabilizing and improving your revenue model, as you are selling new features and add-ons to existing customers without any expenditure on marketing and onboarding.
Customer retention rate is the number of active users of your product/service and will continue to do so. According to Harvard Business School, a five percent increase in the customer retention rate increases sales by up to 25 percent to 95 percent.
It is given by:

15. Existing customer growth rate
This metric defines the efforts of your customer retention and loyalty. It is calculated every month and determines whether your business can retain customers and generate more revenue from them. An increasing rate demonstrates higher sales every month coming from your existing users.
The current Customer growth rate is given by:
Revenue Growth Rate = Recurring revenue rate at end of the month — Recurring revenue rate at the start.
16. Time between purchases
As the name suggests, the time between purchases is a metric that calculates the duration in which a user performs a repeat order/sale. It can be monitored to send promotional emails and newsletters to increase sales at the right opportunity.
It is an important retention metric that allows you to understand the happiness level of your customers and provides insights into the users spending frequency.
This metric helps you to optimize marketing strategies and campaigns based on user analytics.
It is calculated using:

17. Loyal customer rate
Loyal customer rate is a metric that enables you to calculate the number of customers executing repeat orders or purchasing multiple services/add-ons. It displays the loyal customer base related to your product/service when represented in terms of percentage.
In a real world scenario, maintaining a high loyal customer rate gradually increases your sales. Based on marketing metrics, the probability of selling to an existing customer is 14 times more as compared to a new customer.
Loyal Customer Rate is given by:

Wrapping up
According to Lincoln Murphy:
"Customer success is simply ensuring that your customers achieve their Desired Outcome through their interactions with your company. That's it."
SaaS customer success is crucial as companies work on a subscription-based revenue model. To retain customers and maintain positive revenue growth, you need to amp up your game to satisfy your customer. It is also a significant factor that helps to increase your sales, improve your conversions and reduce churn.
Metrics related to customer success will only give information about any potential issues. Identifying and eliminating the root cause is the only solution for your business to reach new heights.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are quality metrics?
Quality metrics define measurements of your product/service business. Various quality metrics can be calculated to keep track of your company's growth and calculate the present and projected revenue rates.
In addition to this, they can also identify various factors like revenue and customer churn, customer lifetime value etc.
What are DPU and DPO?
DPO(Defects per Opportunity) can be defined as the number of defects reported compared to defect opportunities. DPU(Defects per Units) is the total average of all defects compared to the total number of units.
DPU and DPO metrics are collaboratively used to calculate product performance versus the number of defects.
What are primary and secondary metrics?
Quality metrics are of two categories: primary and secondary. Primary metrics are used to calculate the direct, measurable output for a product or a service. In simple words, you are calculating factors directly related to your business's future revenue and growth projections.
At the same time, secondary keywords help you achieve your goal and relate to factors like quality and satisfaction.







